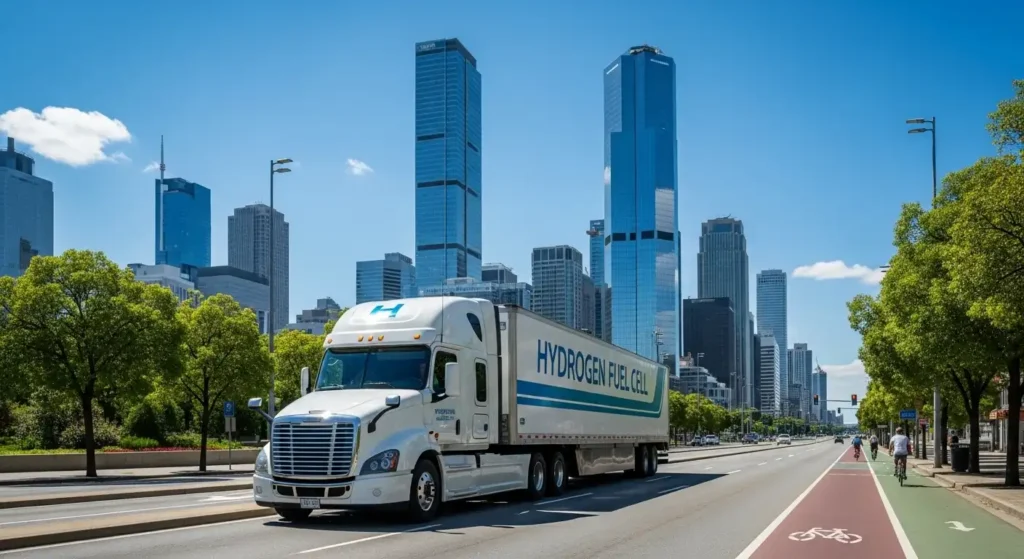
The trucking industry is on the cusp of a revolutionary transformation. As the world grapples with climate change and the push for sustainability intensifies, hydrogen-powered trucks are emerging as a major contender in the battle for zero-emission transportation. With advancements in hydrogen fuel cell technology, these vehicles offer an innovative solution to reduce the environmental impact of freight hauling.
In 2025, hydrogen-powered trucks are expected to take a significant step toward becoming a viable and mainstream alternative to diesel-powered vehicles. These trucks provide a unique set of benefits that make them an attractive option for long-haul freight transportation. From fast refueling to long driving ranges and, of course, zero emissions, hydrogen trucks represent a bright future for the freight industry.
What Are Hydrogen-Powered Trucks?
 Hydrogen-powered trucks are vehicles that use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, which powers an electric motor. The key to their operation is the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, which produces electricity and water vapor, making them an environmentally friendly option. Unlike traditional diesel trucks, which emit carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants, hydrogen trucks release only water vapor as their byproduct, contributing to cleaner air and a reduction in greenhouse gases.
Hydrogen-powered trucks are vehicles that use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, which powers an electric motor. The key to their operation is the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, which produces electricity and water vapor, making them an environmentally friendly option. Unlike traditional diesel trucks, which emit carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants, hydrogen trucks release only water vapor as their byproduct, contributing to cleaner air and a reduction in greenhouse gases.
Hydrogen fuel cell technology has been around for a while, but recent advancements in efficiency, cost, and infrastructure are making hydrogen-powered trucks a practical alternative for freight transportation. In 2025, we expect to see these trucks gain a larger share of the market, particularly for long-haul trucking, where electric trucks might face challenges due to range limitations.
Key Benefits of Hydrogen Trucks
-
Zero Emissions
The most significant advantage of hydrogen trucks is their zero-emission operation. Hydrogen trucks produce no harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), or particulate matter (PM), making them a cleaner alternative to traditional diesel-powered trucks. With governments worldwide setting stricter emissions standards, adopting hydrogen-powered trucks can help the freight industry meet these goals and significantly reduce the sector’s carbon footprint.
The absence of harmful emissions makes hydrogen trucks an attractive option for cities and regions with strict air quality regulations. For instance, hydrogen-powered trucks can operate in areas with low-emission zones without facing penalties or restrictions.
-
Long Driving Range
Hydrogen-powered trucks offer a long driving range compared to battery-electric trucks, which is essential for long-haul freight. While battery-electric trucks are limited by the capacity of their batteries, hydrogen trucks can travel much farther on a single tank of hydrogen. This makes them a perfect solution for freight companies that operate over long distances and need to avoid the downtime associated with long charging times.
The range of a hydrogen truck depends on the size of the hydrogen fuel tank and the efficiency of the fuel cell, but many hydrogen trucks in development today are capable of traveling up to 500 miles or more on a single refueling.
-
Fast Refueling Times
Hydrogen trucks offer a major advantage over battery-electric trucks when it comes to refueling time. While it can take several hours to charge a battery-electric truck, hydrogen trucks can be refueled in a matter of minutes, similar to traditional diesel trucks. This quick refueling capability allows freight companies to minimize downtime and keep their operations running smoothly.
For long-haul drivers, fast refueling times are a crucial factor in choosing hydrogen trucks over other types of zero-emission vehicles. Refueling a hydrogen truck can typically take around 15-20 minutes, which is significantly faster than the several hours it takes to fully charge an electric truck.
-
Energy Efficiency
Hydrogen fuel cells are highly efficient at converting hydrogen into electricity. In fact, hydrogen trucks typically have higher energy efficiency than traditional diesel trucks, offering more miles per unit of energy. This efficiency means hydrogen trucks can go farther on less fuel, making them not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective in the long term.
Furthermore, hydrogen fuel cell technology continues to improve. As fuel cells become more efficient, hydrogen-powered trucks will deliver even greater performance, providing higher energy output and extending the vehicles’ range.
Challenges Facing Hydrogen Trucks
Despite the many benefits of hydrogen-powered trucks, there are still several obstacles to their widespread adoption. These challenges include the cost of fuel cell technology, the need for refueling infrastructure, and the production of hydrogen itself.
-
Infrastructure Development
One of the main challenges for hydrogen trucks is the lack of a widespread hydrogen refueling infrastructure. While electric vehicle charging stations are expanding rapidly, hydrogen refueling stations are still limited, especially in remote areas. For hydrogen trucks to become a viable alternative for long-haul transportation, a robust network of refueling stations is essential.
Governments and private companies are investing in hydrogen infrastructure, and the number of hydrogen refueling stations is expected to grow significantly over the next few years. However, the pace of infrastructure development must accelerate to meet the demand for hydrogen trucks.
-
High Initial Costs
Hydrogen trucks are more expensive than traditional diesel trucks and battery-electric trucks due to the cost of hydrogen fuel cell technology. The materials required for fuel cells, such as platinum, are expensive, and the manufacturing process is complex.
However, as hydrogen fuel cell technology advances and economies of scale are realized, the cost of producing hydrogen-powered trucks is expected to decrease. In the meantime, government incentives and subsidies may help offset the higher upfront costs for businesses looking to adopt hydrogen trucks.
-
Hydrogen Production and Storage
 Hydrogen must be produced and stored before it can be used as a fuel. While hydrogen can be produced from water using renewable energy sources, most hydrogen today is still produced using natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming (SMR). This process releases carbon dioxide, which offsets some of the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel.
Hydrogen must be produced and stored before it can be used as a fuel. While hydrogen can be produced from water using renewable energy sources, most hydrogen today is still produced using natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming (SMR). This process releases carbon dioxide, which offsets some of the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel.
Green hydrogen, which is produced using renewable electricity from sources like wind and solar, offers a cleaner alternative, but the technology to produce green hydrogen is still developing. Additionally, hydrogen needs to be stored at high pressure or in liquid form, requiring specialized equipment that adds to the overall cost.
-
Public Perception and Regulation
Public perception of hydrogen technology also plays a role in the adoption of hydrogen trucks. Concerns over safety, fuel efficiency, and the long-term viability of hydrogen-powered trucks may slow the acceptance of this technology. Regulatory frameworks will need to evolve to support the transition to hydrogen-powered transportation, ensuring safety standards and providing incentives for adoption.
The Road Ahead: The Future of Hydrogen-Powered Trucks
Despite the challenges, hydrogen trucks are poised to become a significant part of the future of freight transportation. Major manufacturers, including Nikola, Toyota, and Hyundai, are already developing and testing hydrogen-powered trucks, and the industry is seeing increasing investments from both governments and private companies. With growing environmental awareness and regulatory pressure, the transition to hydrogen-powered trucks is accelerating.
As technology advances and the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling expands, hydrogen trucks will become more accessible to businesses, offering an efficient and sustainable solution for long-haul freight.
Conclusion:
The future of freight transportation is shifting towards hydrogen-powered trucks. These vehicles offer a promising solution for reducing emissions, improving energy efficiency, and revolutionizing long-haul transportation. While challenges remain, including infrastructure development and high initial costs, the progress made so far signals a bright future for hydrogen-powered trucks in 2025 and beyond.
As the trucking industry continues to evolve, hydrogen-powered trucks will play a key role in achieving zero-emission goals, helping to reduce the environmental impact of freight transportation. For businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve and embrace sustainable practices, hydrogen-powered trucks represent the future of freight logistics.